
Theory Behind the Medicine

Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has a rich and complex history of over two
thousand years. It developed not from the scientific method, but from the
philosophical constructs of Yin-
Yin-
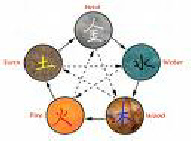
Five Element Theory provides a framework for understanding all processes of nature through the interactions and transformations of five creative forces: fire, earth, metal, water and wood. Each element has its own distinguishing, unique characteristics. For example, fire is warm and upward rising while water is cool, nourishing and descending. The qualities of creating, transporting and receiving pertain to the earth element. Clearing, descending and contracting characterize the metal element. Wood includes all things associated with growth and ascension. The elements interact and strive to maintain relative balance and, thus, harmony is achieved.
The 12 Main Organs

In terms of health and medicine, these theories apply the phenomena and laws of nature to the physiological functions and pathological changes of the human body. According to Chinese Medicine there are 12 main organs, each with its own distinct energetic pathway in the body. These paths are called channels or meridians.
The yin organs of the body (lung, spleen, heart, kidneys, pericardium and liver)
are associated with storing functions, while the yang organs (large intestine, stomach,
small intestine, urinary bladder, triple burner and gallbladder) are more active
and involved in the digestion and elimination processes. For every yin organ there
is a corresponding yang organ; each yin-
Five Element Theory


Traditional Chinese Medicine
with
Aiesha Abel
Licensed Acupuncturist, MSTOM